Getting Arduino to say 'hello' world.
Disclaimer. There are generic tutorials from the internet and beggining Arudino books, all of the images are my own.
- Install the Arduino software
- Example 01: Blinking LED . Its like Hello World for Arduino
- Example 02: Using a Pushbutton to control the LED.
- Example 03: Using PWN to control the LED.
- Example 04: Using an Analog Input.
- Example 05: Sending Stuff to the serial port.
Install Arduino Software
- Download latest software from Arduino.cc. From http://arduino.cc/en/Main/Software . Arduino 0016
- Install onto your computer. I keep mine in the C:/ Directory.
- Run Arduino.exe from C:/Arudino/arduino-0016/arduino.exe
- The loaded Arduino Enviroment.
- Plug in your Arduino.
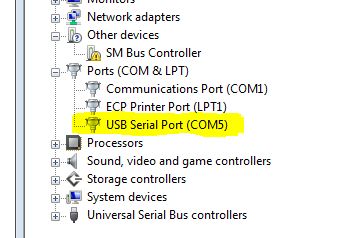
- Find the COM Port of the Arduino.
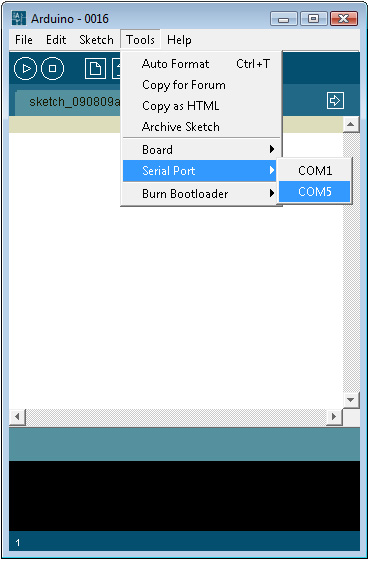
- Setting the COM port in Arudino Programe
Example 01: Blinking LED . Its the 'Hello World' of Arduino.
- Type out the code.
#define LED 13 // LED connected to // digitial pin 13. void setup() { pinMode(LED, OUTPUT); } void loop() { digitalWrite(LED, HIGH); // turns the LED on delay(1000); // waits for a second digitalWrite(LED, LOW); // turns the LED off delay(1000); // waits for a second } - Verify the code.
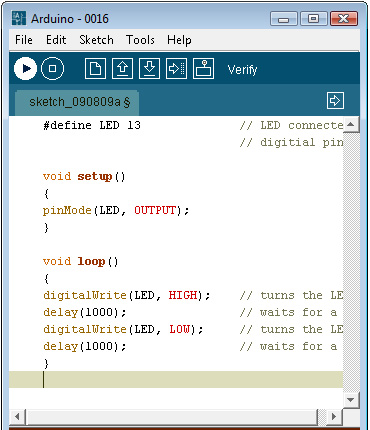
- Upload Code.
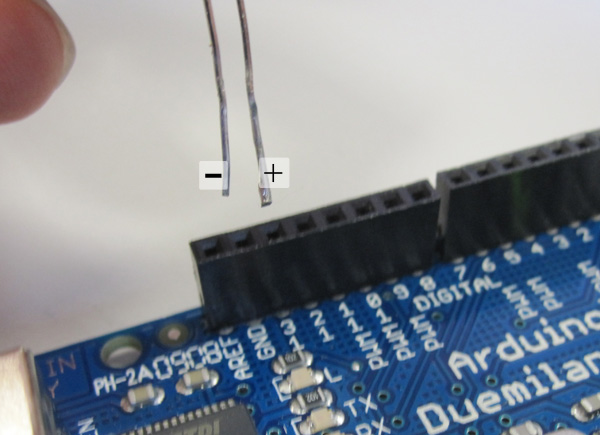
- Insert LED
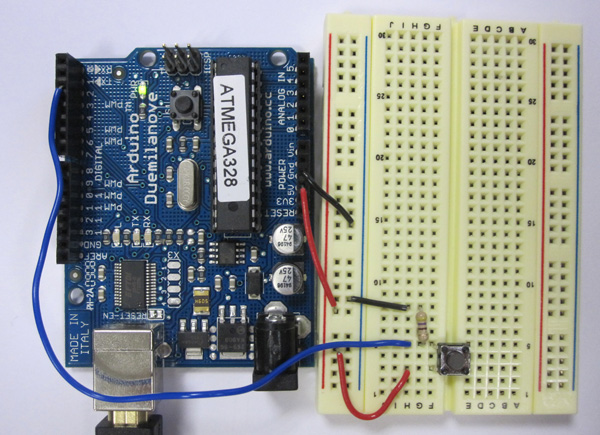
Example 02: Using a Pushbutton to Control the LED.
#define LED 13 // LED connected to
// digitial pin 13.
#define BUTTON 2 // in input for the button
int val = 0; //this value store the button state
void setup() {
pinMode(LED, OUTPUT);
pinMode(BUTTON, INPUT);
}
void loop() {
val = digitalRead(BUTTON); //Reads the buttons and stores it.
// Uses an IF statement to see if BUTTON is pressed.
if (val == HIGH ) {
digitalWrite(LED, HIGH); //turn LED On.
} else {
digitalWrite(LED, LOW);
}
}
}
Example 2.
#define LED 13 // LED connected to
// digitial pin 13.
#define BUTTON 2 // in input for the button
int val = 0; //this value store the button state
int state = 0; // 0 = LED off while 1 = LED on.
void setup(){
pinMode(LED, OUTPUT);
pinMode(BUTTON, INPUT);
}
void loop(){
val = digitalRead(BUTTON); //Reads the buttons and stores it.
// Uses an IF statement to see if BUTTON is pressed.
// and changes it state
if (val == HIGH {
state = 1 - state;
}
if (state == 1) {
digitalWrite(LED, HIGH); //Turn LED on.
} else {
digitalWrite(LED, LOW);
}
}
Example 3. Turn on LED when the button is pressed and keep it on after it is released. Including simple de-bouncing.
#define LED 13 // LED connected to
// digitial pin 13.
#define BUTTON 2 // in input for the button
int val = 0; //this value store the button state
int state = 0; // 0 = LED off while 1 = LED on.
int old_val = 0; // stores the previous val.
void setup(){
pinMode(LED, OUTPUT);
pinMode(BUTTON, INPUT);
}
void loop() {
val = digitalRead(BUTTON); //Reads the buttons and stores it.
// Uses an IF statement to see if BUTTON is pressed.
// and changes it state
if ((val == HIGH ) && (old_val == LOw)) {
state = 1 - state;
delay(10);
}
old_val = val; // val is old, and stored in the old_val.
if (state == 1) {
digitalWrite(LED, HIGH); //Turn LED on.
} else {
digitalWrite(LED, LOW);
}
}
Example 03:Using PWN to control the LED.
An example that fades an LED in and out. Looks like Apple?
#define LED 9 // LED connected to
// digitial pin 9.
int i = 0; //this value store the button state
void setup(){
pinMode(LED, OUTPUT);
}
void loop(){
for (i = 0; i < 255; i++) { //loops from 0 to 254. Fades Up.
analogWrite(LED, i);
delay(10); //Wait 10ms because analogWrite would otherwise
// be instantaneous.
}
for (i = 255; i > 0; i--) { //loops from 255 to 1. Fade Down.
analogWrite(LED, i); // Gives the LED power.
delay(10);
}
}
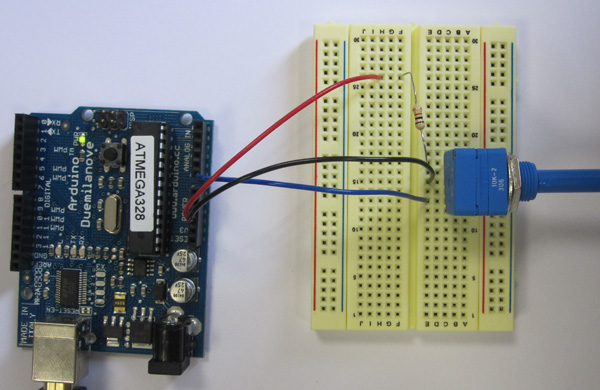
Example 04: Using an Analog Input. Using an LDR
The more resistance the longer the light will come on.
/*
Analog Input
Demonstrates analog input by reading an analog sensor on analog pin 0 and
turning on and off a light emitting diode(LED) connected to digital pin 13.
The amount of time the LED will be on and off depends on
the value obtained by analogRead().
The circuit:
* LDR attached to analog input 0
*/
int sensorPin = 0; // select the input pin for the potentiometer
int ledPin = 13; // select the pin for the LED
int sensorValue = 0; // variable to store the value coming from the sensor
void setup() {
// declare the ledPin as an OUTPUT:
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// read the value from the sensor:
sensorValue = analogRead(sensorPin);
// turn the ledPin on
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH);
// stop the program for milliseconds:
delay(sensorValue);
// turn the ledPin off:
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW);
// stop the program for for milliseconds:
delay(sensorValue);
}
Example 05:Sending data to the serial port.
Example 05: Sending data to the serial port.
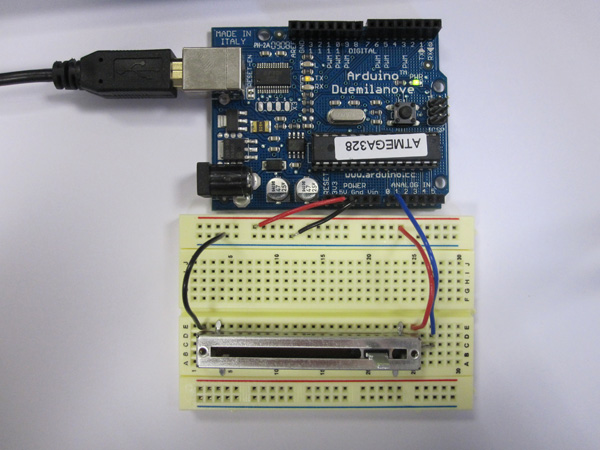
Example 04: Using an Analog Input.
#define SENSOR 1
int val = 0;
void setup(){
Serial.begin(9600); //Opens a serial port.
}
void loop(){
val = analogRead(SENSOR);
Serial.printIn(val);
delay(100); //Wait 100ms bewteen each send.
}